Business and data analysts are two key roles shaping how organisations make decisions and adapt to change. While their contributions often overlap, their focus and skillsets differ significantly. Choosing between these careers requires understanding their responsibilities and how they align with your interests and strengths.
In this article, we will explore the differences between a business analyst vs. a data analyst, from their day-to-day roles and the skills they need to career growth opportunities. Whether you’re an aspiring professional or considering a career switch, this guide will help you decide which path is right for you.
Let’s start by understanding each professional’s unique role in an organisation.
What Does a Business Analyst Do?
We’ve discussed the role of a business analyst in detail in our previous blog post. For an in-depth understanding, check out our article on What Does a Business Analyst Do? But let’s take a quick look at the essentials here.
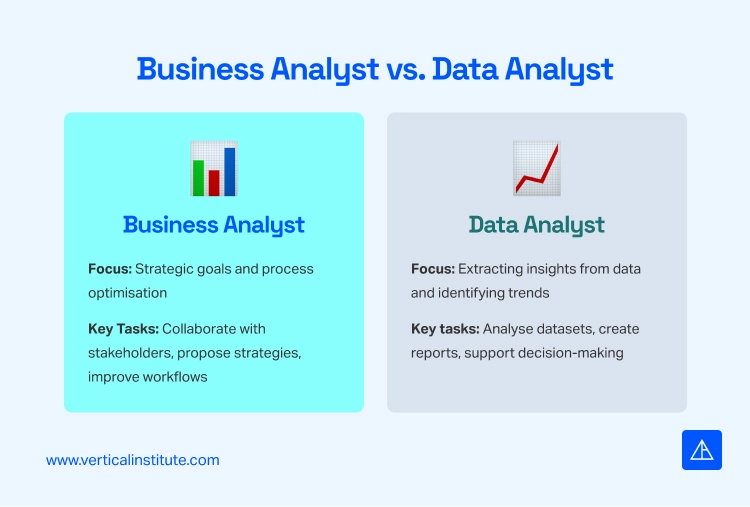
A business analyst links an organisation’s goals and technical solutions. Their work involves identifying business needs, analysing processes, and proposing strategies to improve efficiency and outcomes.
Key responsibilities of a business analyst include:
| 🔍 Conduct Market Research | Investigating market trends and performing competitive analysis to identify opportunities and threats. |
| 💬 Facilitate Communication | Bridging the gap between technical teams and non-technical stakeholders to ensure smooth collaboration. |
| 📜 Define and Validate Requirements | Documenting business requirements and ensuring proposed solutions align with organisational goals. |
| 📊 Analyse and Recommend Improvements | Evaluating processes and suggesting data-driven strategies to enhance efficiency and performance. |
As Coursera highlights, business analysts are instrumental in ensuring that projects align with organisational objectives. Their expertise is highly sought after in industries like finance, healthcare, and technology, where efficient decision-making is paramount.
What Does a Data Analyst Do?
Data analysts focus on extracting meaningful insights from raw data to support business decisions. Their highly analytical role requires them to work with datasets to identify trends, measure performance, and forecast outcomes. Data analysts often use SQL, Python, and Tableau to clean, analyse, and visualise data.
Typical tasks for a data analyst include:
| 📂 Collect and Organise Data | Gathering data from multiple sources and ensuring it is structured for analysis. |
| 📈 Perform Statistical Analysis | Using statistical methods to uncover trends, correlations, and patterns in data. |
| 📊 Create Dashboards and Reports | Developing visual and written reports to present insights to stakeholders. |
| 🧠 Support Decision-Making with Insights | Providing data-driven recommendations to inform business strategies and actions. |
According to Indeed, data analysts contribute to a company’s success by transforming data into actionable intelligence. They ensure that leaders can make informed decisions based on reliable metrics.
Related Article: Power BI vs Tableau: What is the Best Data Visualisation Tool to Learn
Educational Background and Experience
Education plays a crucial role in shaping the careers of both business analysts and data analysts. While their roles require distinct skill sets, both paths benefit from targeted academic foundations and professional certifications that strengthen their expertise.
Educational Pathways for Business Analysts
A business analyst typically requires a strong business, management, or information technology foundation.
- Common degrees include business administration, finance, or computer science.
- Some professionals pursue postgraduate qualifications to specialise or gain a competitive advantage in the job market.
- Certifications, such as the Certified Business Analysis Professional (CBAP) or Agile-related credentials, can enhance one’s skill sets and career prospects.
- Employers value these certifications because they focus on structured and methodical problem-solving approaches.
Related Article: Exploring Business Analyst Courses for Beginners in Singapore
Educational Pathways for Data Analysts
A data analyst typically comes from a quantitative background with degrees in mathematics, statistics, computer science, or economics. These fields provide the analytical foundation to work with large datasets and uncover meaningful insights.
- Proficiency in programming languages such as Python and R is crucial, along with experience in data tools like SQL, Tableau, and Excel.
- Employers widely recognise certifications such as the Microsoft Certified Data Analyst Associate, the Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate, or the Data Analytics and Advanced Data Analytics courses at Vertical Institute. Vertical Institute’s certification programme is beginner-friendly, allowing individuals without prior experience to enrol. It equips learners with industry-relevant skills, focusing on tools like SQL, Tableau, and Excel, preparing them for data-driven roles.
- These certifications and training pathways validate technical expertise and open doors to advanced analytics and data science roles.
Educational Pathways: Business Analyst vs. Data Analyst
| Business Analyst | Data Analyst | |
| Typical Degrees | Business Administration, Finance, IT | Mathematics, Statistics, Computer Science |
| Key Skills | Business Analysis, Communication | Data Tools (SQL, Tableau), Programming |
| Certifications | CBAP, Agile-related credentials | Microsoft Data Analyst, Google Analytics, Vertical Institute Data Analytics, and Advanced Data Analytics courses |
| Career Readiness | Structured, methodical problem-solving | Beginner-friendly certification options are available |
Related Article: Entry-Level Data Analyst Salary in Singapore: A Guide to Earning Potential
Career Trajectories and Advancement
Business and data analysts follow unique career paths that reflect their respective roles and expertise. Below, we outline typical career trajectories for each.
Career Path for Business Analysts
- Entry-level roles include Junior Business Analyst, Operations Analyst, or Business Consultant.
- Progression to Senior Business Analyst involves managing complex projects and aligning strategies with business goals.
- Specialisations include Product Management, Business Intelligence, or IT Systems Analysis.
- Leadership roles like Business Analysis Manager or Chief Business Analyst focus on mentoring and strategic initiatives.
Career Path for Data Analysts
- Entry-level roles include Data Technician or Reporting Analyst, focusing on data collection and cleaning.
- Growth leads to Senior Data Analyst, handling advanced analysis, predictive modelling, and data visualisation.
- Advanced roles include Data Scientist, Machine Learning Specialist, or Statistician.
- Leadership opportunities, such as Analytics Manager or Chief Data Officer (CDO), shape organisational data strategies.
Career Pathways: Business Analyst vs. Data Analyst
| Business Analyst | Data Analyst | |
Entry-Level Roles | Junior Business Analyst, Operations Analyst | Data Technician, Reporting Analyst |
Mid-Level Roles | Senior Business Analyst, Product Manager | Senior Data Analyst, Data Scientist |
Specialisations | Product Management, Business Intelligence | Machine Learning, Statistical Modelling |
| Leadership Roles | Business Analysis Manager, Chief Business Analyst | Analytics Manager, Chief Data Officer (CDO) |
Finding Your Ideal Career Path
Whether you become a business analyst or a data analyst depends on your interests, strengths, and long-term goals.
- Choose a Business Analyst role if you enjoy strategic planning, problem-solving, and working closely with stakeholders to drive organisational improvements.
- Opt for a Data Analyst role if you thrive on working with numbers, uncovering patterns, and providing actionable insights based on data.
Both paths offer strong career growth, lucrative opportunities, and the ability to impact your organisation meaningfully. Reflect on your skills and ambitions to determine which role aligns with your aspirations.
Conclusion
Both business analysts and data analysts play crucial roles in helping organisations thrive. While their focus and skill sets differ, both careers offer rewarding opportunities for professionals ready to undertake challenging and impactful work.
Whichever path you choose, investing in education and certifications is key to staying competitive in these high-demand fields. With the proper foundation and dedication, you can build a thriving career as either a business analyst or a data analyst.
Discover Your Earning Potential with Our Free Salary Calculator
How much can you earn as a business analyst or data analyst? Use our free salary calculator to get personalised insights into your potential salary based on industry trends and experience.
SALARY CALCULATOR
Discover how much you can earn in your dream role.
Don’t just dream about your ideal career—plan for it. Explore options, set realistic goals, and equip yourself with the right skills through Vertical Institute’s courses. Start your journey today!
About Vertical Institute
Vertical Institute is shaping the future of work by preparing individuals for tomorrow’s job market. Our courses and certification focus on teaching essential skills and nurturing the next generation of innovators and leaders.
As an Approved Training provider (ATO) accredited by SkillsFuture Singapore (SSG) and the Institute of Banking & Finance Singapore (IBF), our courses adhere to the highest standards. They are government-subsidised and eligible for SkillsFuture Credits or NTUC UTAP Funding.



